Nanotech in agriculture helps boost your crop yields and cut waste by improving nutrient delivery with controlled release systems, making fertilizers more efficient. It also extends pesticide effectiveness, reducing application frequency and environmental runoff. Soil and water treatments with nanomaterials enhance resource management, while seed coatings improve germination and stress resistance. As you explore further, you’ll discover how these innovations are shaping sustainable farming and addressing global food security challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Nanotech enhances nutrient delivery and controlled release, increasing crop yields by 20-30% while reducing fertilizer waste.
- Nanoparticle-based pesticides and herbicides offer longer-lasting effects, lowering chemical application frequency by up to 70%.
- Seed coatings with nanomaterials improve germination, early growth, and stress resilience, leading to healthier crops and higher productivity.
- Nano-enabled soil and water treatments improve resource efficiency, minimize environmental runoff, and support sustainable water management.
- Precision delivery systems and nanosensors optimize input use, reducing waste and supporting site-specific, sustainable farming practices.
Enhanced Nutrient Delivery and Efficiency
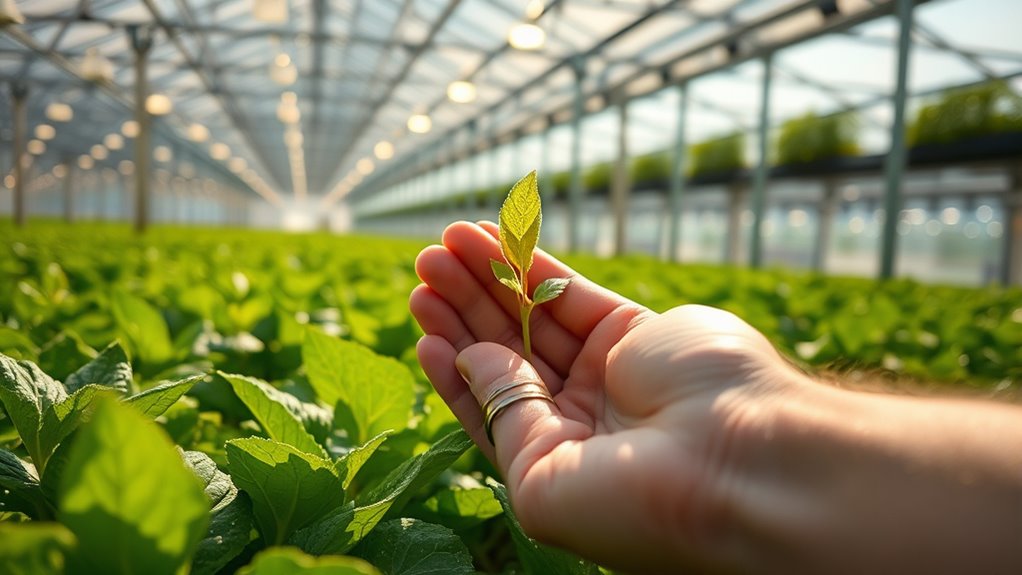

Nanotech-enabled fertilizers markedly improve nutrient delivery by controlling release rates and targeting soil and plant tissues directly. You’ll notice these formulations release nutrients gradually, matching plant uptake demands more efficiently than traditional fertilizers. This targeted approach minimizes nutrient losses through leaching and runoff, reducing environmental impact. By ensuring nutrients stay where plants need them most, you can achieve higher use efficiency—nitrogen-use efficiency, for example, can rise from around 49% to 69%. You may also apply lower fertilizer amounts, saving costs while maintaining or boosting yields by up to 20-30%. Additionally, nano-fertilizers are compatible with precision agriculture systems, integrating with sensors and variable-rate applicators. This combination allows for site-specific nutrient management, optimizing input use, and supporting sustainable, productive farming practices.
Pesticides and Herbicides With Longer-Lasting Effects
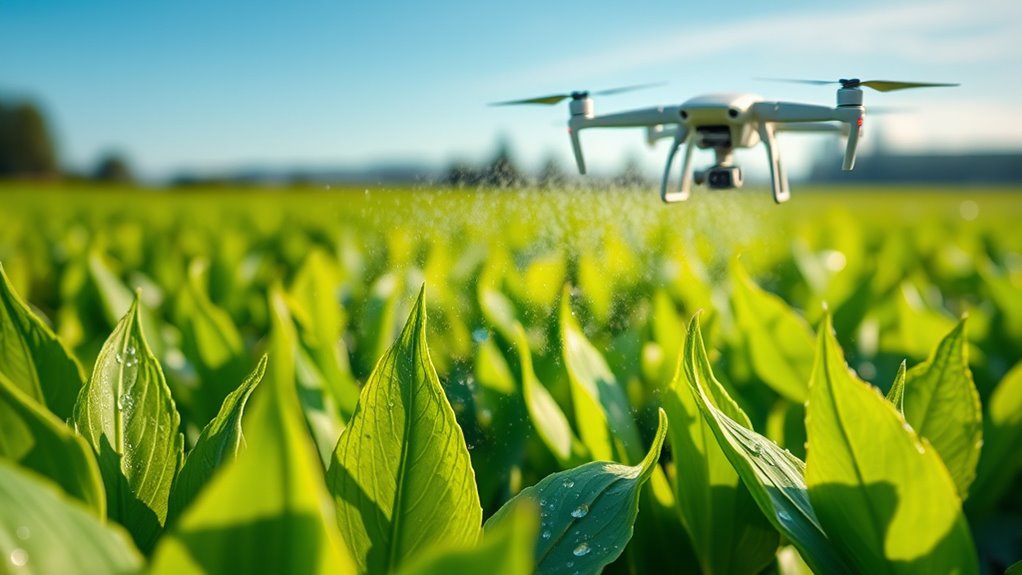

Nanoparticle-based pesticides and herbicides are transforming crop protection by offering longer-lasting activity and improved stability. They release active ingredients slowly, reducing the need for frequent reapplications. Encapsulation helps target pests and weeds more precisely, minimizing off-target effects. These nanoformulations also lower chemical runoff, protecting the environment. You benefit from decreased chemical use—up to 70% in some cases—while maintaining effective pest control. Additionally, multifunctional nano-carriers can deliver nutrients alongside pesticides, consolidating inputs. European cloud innovation is also playing a role in managing agricultural data and monitoring crop health more effectively. Harnessing nanotechnology allows for more efficient and sustainable farming practices. This approach supports regulatory compliance by reducing environmental impacts and adhering to safety standards. Advances in nanomaterial development are further enhancing the effectiveness of these formulations. The use of targeted delivery systems is revolutionizing how pesticides are applied, ensuring minimal environmental footprint. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Conventional Formulations | Nano-Enabled Systems | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence in field | Short-lived | Longer-lasting | Reduced runoff and contamination |
| Application frequency | High | Lower | Lower chemical load |
| Target specificity | Moderate | High | Less non-target damage |
With these advancements, you can protect crops more efficiently and sustainably.
Advanced Soil and Water Quality Management

Enhancing soil and water quality through nanotechnology involves applying engineered nanomaterials to improve resource efficiency and environmental safety. Nanomaterials like nanoclays and bio-based nanolignocellulics boost soil water retention and nutrient adsorption, reducing irrigation needs and nutrient leaching. Nano-enabled water purification systems can adsorb heavy metals and pesticide residues, supporting water reuse and minimizing contamination. Soil amendments with nanoparticles increase cation-exchange capacity, enhancing fertilizer efficiency and lowering runoff risks. Using biodegradable nanomaterials minimizes long-term soil accumulation, protecting ecosystems. These innovations foster drought resilience and cleaner water sources. The development of environmentally safe nanomaterials is crucial to ensure sustainable application and minimize potential ecological risks. Additionally, research into nanotoxicology is essential to understand and mitigate any unintended environmental impacts of nanomaterials. Understanding nanomaterial interactions with soil and water ecosystems is vital for developing responsible and effective agricultural nanotechnologies. Ongoing studies into nanomaterial degradation help ensure that these materials do not persist in the environment longer than necessary. Overall, nanotech offers promising solutions for sustainable soil and water management in agriculture.
Innovative Plant Breeding and Seed Technologies

Nanotech is transforming plant breeding by enabling precise gene editing and faster development of improved crop varieties through nanoparticle delivery systems. You can also enhance seed performance with nano-coatings that boost germination, early growth, and stress resilience. These innovations promise to shorten breeding cycles and increase yields, but regulatory and safety considerations still need addressing. Additionally, understanding the net worth of key industry figures can help inform future investments and innovations in this field. The high pressure and precision of nanotechnology tools also allow for targeted delivery of nutrients and pesticides, reducing waste and environmental impact. Moreover, advances in color accuracy are helping optimize plant growth conditions and monitoring. Regular appliance maintenance plans are essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of equipment used in agricultural technologies, including those employing nanotech solutions. Implementing study techniques can further support the integration of these advanced technologies into sustainable farming practices.
Nano-mediated Gene Editing
Nano-mediated gene editing is transforming plant breeding by enabling precise delivery of genetic materials directly into target cells. Using nanoparticles like gold or carbon nanotubes, you can introduce CRISPR components or other biomolecules more efficiently than traditional methods. This approach reduces reliance on labor-intensive tissue culture steps, speeding up the development of improved crop traits such as disease resistance and stress tolerance. Nano-carriers protect genetic materials from degradation, enhancing transfection accuracy and success rates. You also benefit from lower off-target effects, as the delivery is more targeted. While regulatory frameworks are still evolving, this technology offers a promising route to accelerate breeding programs and reduce costs. Overall, nano-mediated gene editing provides a powerful tool for developing resilient, high-yield crops with greater precision in gene transfer.
Enhanced Seed Coatings
Innovative seed coatings incorporate nanomaterials to improve germination, early growth, and stress resilience. These coatings deliver nutrients, protectants, and growth stimulants directly to seeds, enhancing establishment under challenging conditions. Nanoparticles enable controlled release and targeted delivery, reducing the need for multiple treatments. This precision delivery technology speeds up breeding processes and lowers costs by minimizing tissue culture steps. Seed coatings with nanomaterials also increase seed vigor and uniformity, leading to better crop stands. Here’s a snapshot:
| Coating Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Nutrient-loaded | Faster germination, early vigor |
| Protective nanolayers | Disease resistance, stress tolerance |
| Growth stimulants | Improved seedling development |
| Controlled-release | Sustained nutrient supply |
| Targeted delivery | Reduced chemical use and environmental impact |
Additionally, the use of nanotechnology in seed coatings can improve the efficiency of resource utilization, leading to more sustainable agricultural practices. This advancement supports the development of smart seed treatments that respond dynamically to environmental conditions, further enhancing crop productivity and resilience. A growing body of research indicates that nanomaterials can also enhance the durability and effectiveness of seed coatings over time. Moreover, ongoing innovations in targeted delivery systems facilitate precision agriculture by optimizing resource allocation for specific crop needs.
Market Growth and Adoption Challenges

Despite the promising potential of agricultural nanotechnology to boost yields and reduce inputs, widespread adoption faces significant hurdles. Cost remains a major barrier, especially for smallholders who struggle to afford advanced nano-products. Limited field-scale validation and region-specific formulations hinder confidence in real-world performance. Regulatory uncertainty adds further complexity; many jurisdictions lack clear guidelines, delaying approval and commercialization. Safety and ecotoxicology data are incomplete, raising concerns about long-term environmental impacts and soil health. Additionally, farmers need better extension services and technical support to integrate nanotech solutions effectively. The development of standardized testing protocols and comprehensive lifecycle assessments is crucial for establishing safety and efficacy standards. Without standardized testing, exhaustive lifecycle assessments, and harmonized regulations, scaling up remains a challenge. Overcoming these barriers requires collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and industry to build trust and create accessible, safe, and effective nanotech products. Market dynamics also play a crucial role in influencing the pace of adoption and technological integration. Moreover, fostering public awareness about the benefits and risks of nanotech in agriculture can help facilitate more informed decision-making among stakeholders. Furthermore, ongoing research into environmental safety is essential to address long-term sustainability concerns associated with nanomaterials. Incorporating scientific validation and transparent reporting can further enhance stakeholder confidence and accelerate adoption.
Future Perspectives and Sustainable Development

Advancing sustainable agriculture with nanotechnology depends on addressing current challenges and harnessing future opportunities. You’ll need to prioritize developing biodegradable nanomaterials that minimize environmental impact and guarantee safe soil and water use. Investing in large-scale field trials across diverse agroecologies will help validate effectiveness and build confidence among farmers and regulators. Embracing integrated approaches, like nanosensors and precision delivery systems, can optimize resource use while reducing waste. You should also focus on establishing clear regulatory frameworks and safety standards to support innovation and public acceptance. By aligning research efforts with sustainability goals, you’ll help create resilient agricultural systems that boost yields, lower input costs, and protect ecosystems for future generations. This balanced path will maximize the benefits of nanotech while safeguarding the environment. Incorporating local traditions and indigenous practices can further enhance the acceptance and effectiveness of nanotechnological solutions in diverse communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Nano-Fertilizers Compare Cost-Effectively to Conventional Fertilizers for Small Farmers?
You’ll find nano-fertilizers can be more cost-effective than conventional ones because they boost nutrient use efficiency, reducing the amount you need to apply—sometimes by 20%—and increase yields by up to 30%. They also lower waste and runoff, which means fewer inputs and less environmental impact. While they might have higher upfront costs, the savings in fertilizer use and improved crop productivity make them a smart investment for small farmers over time.
What Are the Long-Term Environmental Impacts of Nano-Materials in Soil Ecosystems?
You might think nano-materials pose minimal risk, but long-term impacts on soil ecosystems remain uncertain. Some studies suggest engineered nanoparticles could alter microbial communities, disrupt nutrient cycling, or accumulate in soil, potentially harming plant health and biodiversity. While biodegradable options show promise, more extensive, long-term research is needed to understand their ecological effects fully. Until then, cautious use and ongoing monitoring are essential to prevent unintended environmental consequences.
Are Nano-Enabled Pesticides Safe for Non-Target Organisms and Human Health?
Nano-enabled pesticides can be safe for non-target organisms and human health if properly designed and regulated. They offer controlled release and targeted delivery, reducing off-target impacts and chemical runoff. However, safety depends on thorough testing, understanding environmental interactions, and establishing standards. You should stay informed about ongoing research, regulatory updates, and risk assessments, as current data gaps mean cautious adoption is essential to protect ecosystems and human health.
How Scalable and Affordable Are Nanosensor Technologies for Widespread Farm Use?
A penny saved is a penny earned, and that rings true for nanosensor tech. While these sensors are becoming more affordable, scaling up for widespread farm use still faces hurdles like high initial costs, calibration needs, and maintaining long-term durability. However, ongoing innovations and mass production are driving down prices. With targeted investments and supportive policies, you can expect nanosensor solutions to become more accessible and practical for farmers across diverse regions soon.
What Regulatory Frameworks Exist Worldwide for Approving Nano-Agriculture Products?
You should know that worldwide regulatory frameworks for nano-agriculture products vary widely. Some regions, like the European Union, are developing strict guidelines emphasizing safety and environmental impact, while others have limited regulations or are still drafting policies. You need to stay informed about regional standards, as approvals often require thorough safety assessments, environmental risk evaluations, and standardized testing. Managing these frameworks is vital for successful product commercialization and ensuring safety.
Conclusion
Imagine if nanotech truly transforms agriculture as some experts claim—that it could double yields and slash waste. While promising, skeptics argue that long-term environmental impacts remain uncertain. You should question whether these tiny innovations will deliver on their hype or pose unforeseen risks. As you consider adopting such technologies, remember that thorough research and cautious implementation are key. The future of farming may hinge on whether nanotech’s potential outweighs its challenges.